Home » Health News »
First aid tips: How to help a person with burn injuries
The first thing one needs to do is remove the source of heat, look for associated trauma and keep any kind of clothing from coming in touch with the skin.
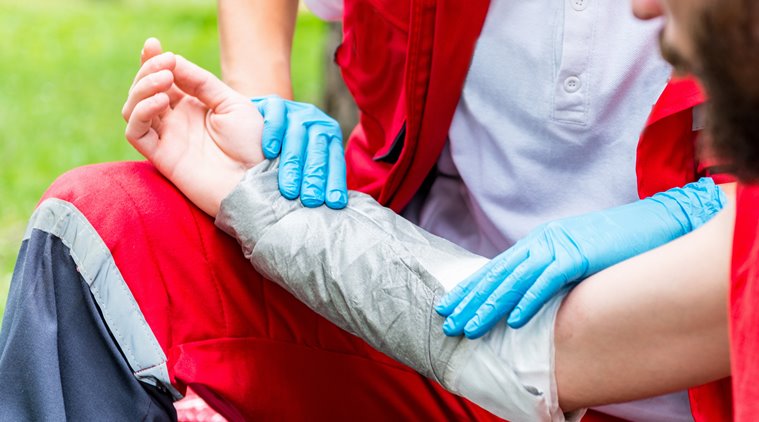
Burns can often occur while working in the kitchen and can cause a minor injury, but they can also be life-threatening if the injuries are more serious. They are usually categorised as first, second and third degree burns, according to the severity. Which is why ensuring adequate fire safety precautions at home and even outside is extremely important. It is also essential to educate children about how to keep themselves safe from such dangers.
According to the World Health Organisation, a burn is an injury to the skin or other organic tissue primarily caused by heat or due to radiation, radioactivity, electricity, friction or contact with chemicals. Skin injuries due to ultraviolet radiation, radioactivity, electricity or chemicals, as well as respiratory damage resulting from smoke inhalation, are also considered to be burns.
The severity of a burn is determined by how deep the wound is. To help you keep yourself safe from any fire-related injury, Dr Anup Dhir, senior cosmetic surgeon, Apollo hospital, Delhi shares a few simple first aid tips:
ALSO READ | Health Ministry proposes minimum standards for clinical establishments
*Everybody should be aware of the first aid procedures, which, if administered on time can reduce the severity of the injury.
*The first thing one needs to do is remove the source of heat, look for associated trauma and keep clothing from coming in touch with the skin. However, it is important to not try and remove clothing which has got stuck to the skin. If a person’s clothes have caught fire, one needs to put out the flames first. Do not allow the flames to spread. Lay the person down on the ground and wrap them tightly with a thick piece of cloth and smother the flame by gently rolling the victim or by patting over the covering.
*Try and cool down the burn with cold, clean water as soon as possible. Cold water eases the pain, removes the heat and lowers the temperature in the injured tissue. This prevents further injury to the skin. Cooling can be effective for about 30 minutes to an hour after the injury. In case of an extensive burn, cool for no longer than five minutes, especially in babies and children. Wrap the wound in a clean towel and take the patient to medical care facility for treatment.
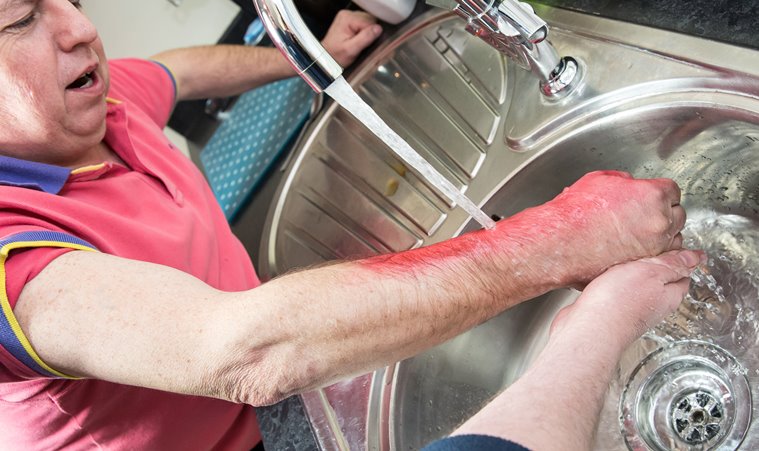
*The initial management of a burn patient involves resuscitation of the patient for shock, taking care of the fluid balance and preventing infection. The long term management involves preventing the formation of contractures as any other subsequent deformity.
*In case of a chemical burn, wash the affected part with cold running water for 10-15 minutes to remove all traces of the chemical. At the same time remove any contaminated clothing. Make sure the patient is transported to the nearest hospital without any delay.
Another way to treat a burn injury is through the process of skin grafting, which is popular across the United States of America, Europe and is also done at a few centres in India. The advantages of this technique include:
*It reduces the chances of getting an infection. Our skin is our greatest defence against infection as it prevents the infecting organism from entering our body. When barrier is lost due to a burn, the patient becomes susceptible to infection. Earlier the skin is restored (by grafting), less will be the chances of infection.
*It prevents the formation of contractures and any deformities. It is very useful for burns involving the joints, face and hands. If a burn wound is allowed to heal without intervention then the skin heals with contraction, and forms contractures which can lead to serious deformities and disability besides being cosmetically demoralising for the patient.
* Earlier, contractures were allowed to form and treated with skin grafting at a later date. These days early skin grafting can be done within the first week (especially for face, hand and joint surface burns ) if the patient is stable, which prevents the formation of contractures. Skin grafting involves taking skin from the healthy areas of the body (usually the thigh area if it is not involved ), meshing it and putting it on the wound. The donor area also heals as new skin grows.
Source: Read Full Article


