Home » Health News »
Common tumor inhibitor drug triggers unfavorable immune effects
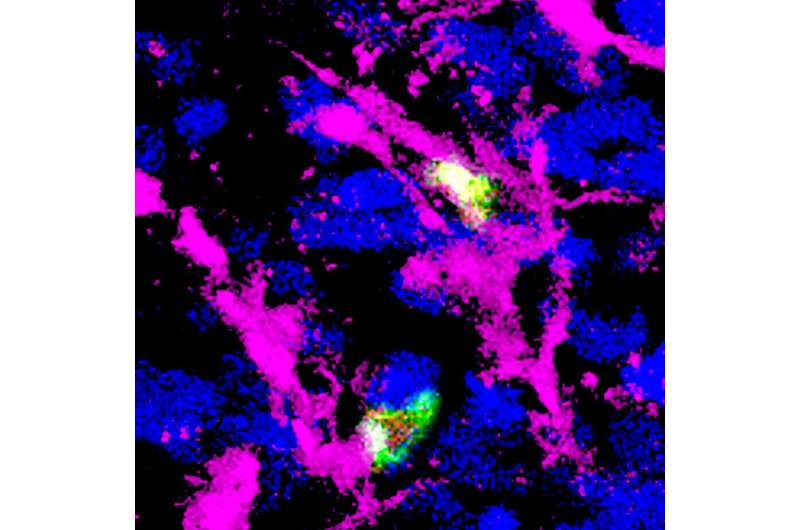
Cancer immunotherapy involving drugs that inhibit CTLA-4 also activates an unwanted response that may self-limit its efficacy in fighting tumors, according to a new study led by Francesco Marangoni, Ph.D., assistant professor of physiology & biophysics and member of the Institute for Immunology at the University of California, Irvine. Study results are published online in the journal Cell.
Using a person’s own immune system—immunotherapy—to treat cancer may also stimulate T regulatory cells, which are essential for preventing autoimmunity, in which the body attacks healthy cells and tissue, but limit tumor control. Some anticancer drugs of the checkpoint inhibitor family block the molecule CTLA-4 and activate both the CD8 and CD4 effector T cells, which kill cancer. Using intravital microscopy, a technique that allows imaging of cells within a living organism, researchers found that CTLA-4 blockage also causes the expansion of T regulatory cells, decreasing the effect of immunotherapy.
“Much of our knowledge of the mechanisms by which immunotherapy works is focused on the positive aspects of the body’s reaction, but that treatment targets the whole immune system. In this study, we investigated how Treg cells are activated within the tumor mass. We discovered that Treg cells are continuously activated in cancer. In turn, they use CTLA-4 to instruct dendritic cells to become inefficient activators of the immune system. Upon CTLA-4 inhibition, dendritic cells become more active and promote the function of effector and regulatory T cells at the same time. This has the potential of limiting efficacy and may explain the failure of immunotherapy in some patients,” said Marangoni, corresponding author on the study.
Source: Read Full Article



