Home » Health News »
Researchers show that DNA topological problems may cause lymphoma
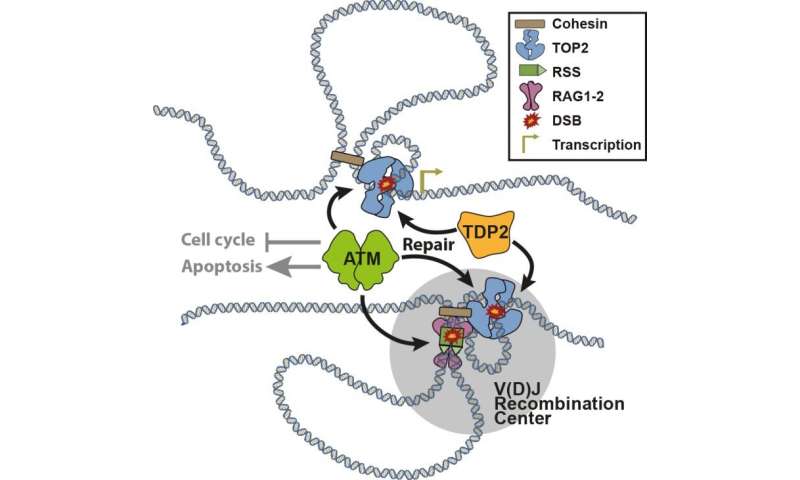
Researchers from the Spanish National Cancer Research Centre (CNIO), Madrid, and the Andalusian Molecular Biology and Regenerative Medicine Centre (Cabimer), Seville, published a paper in Nature Communications that shows that DNA topological problems may cause endogenous DNA breaks that have a causal relationship with cancer.
The starting point of the study, entitled “Endogenous topoisomerase II-mediated DNA breaks drive thymic cancer predisposition linked to ATM deficiency,” is that, during lymphocyte maturation, a number of genomic regions must find each other and rearrange to generate the DNA sequence variability required for the immune response. “This study demonstrates that movements and changes in the 3-D genome structure create knots and tangles in DNA that, during their resolution, are a source of chromosomal breakage,” says Felipe Cortés Ledesma, lead author and Head of the Topology and DNA Breaks Group at CNIO. “In conditions in which the response to these breaks is impaired, chromosomal translocations that may be associated with lymphoma development can occur. Actually, this is true upon mutations in the ATM gene, which are very common in haematological malignancies and the cause of the lymphoma-prone syndrome ataxia telangiectasia,” he adds.
Ataxia telangiectasia (A-T), also referred to as Louis-Barr syndrome, is a genetic disease caused by ATM gene mutation and inherited in an autosomal recessive pattern. The gene is located on the long arm of chromosome 11. The Spanish Ataxia Telangiectasia Association (AEFAT) funded part of this study, published today and co-authored by Felipe Cortés Ledesma, Alejandro Álvarez-Quilón and José Terrón Bautista, from Cabimer.
As described in the abstract of the paper, the ATM kinase is a master regulator of the DNA damage response to double-strand breaks and a well-established tumour suppressor whose loss is the cause of the neurodegenerative and cancer-prone syndrome A-T. A-T patients are particularly predisposed to develop lymphoid cancers. “Our results show a strong causal relationship between topological problems and cancer development (…), confirming these lesions as a major driver of ATM-deficient lymphoid malignancies, and potentially other conditions and cancer types,” the authors say in the paper.
Source: Read Full Article



