Home » Health News »
AI accurately identifies normal and abnormal chest X-rays
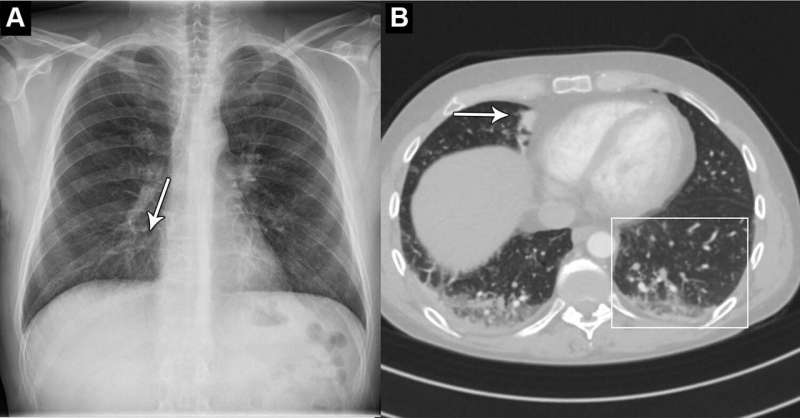
An artificial intelligence (AI) tool can accurately identify normal and abnormal chest X-rays in a clinical setting, according to a study published in Radiology.
Chest X-rays are used to diagnose a wide variety of conditions to do with the heart and lungs. An abnormal chest X-ray can be an indication of a range of conditions, including cancer and chronic lung diseases.
An AI tool that can accurately differentiate between normal and abnormal chest X-rays would greatly alleviate the heavy workload experienced by radiologists globally.
“There is an exponentially growing demand for medical imaging, especially cross-sectional such as CT and MRI,” said study co-author Louis Lind Plesner, M.D., from the Department of Radiology at the Herlev and Gentofte Hospital in Copenhagen, Denmark. “Meanwhile, there is a global shortage of trained radiologists. Artificial intelligence has shown great promise but should always be thoroughly tested before any implementation.”
For this retrospective, multi-center study, Dr. Plesner and colleagues wanted to determine the reliability of using an AI tool that can identify normal and abnormal chest X-rays.
Researchers used a commercially available AI tool to analyze the chest X-rays of 1,529 patients from four hospitals in the capital region of Denmark. Chest X-rays were included from emergency department patients, in-hospital patients and outpatients. The X-rays were classified by the AI tool as either “high-confidence normal” or “not high-confidence normal” as in normal and abnormal, respectively.
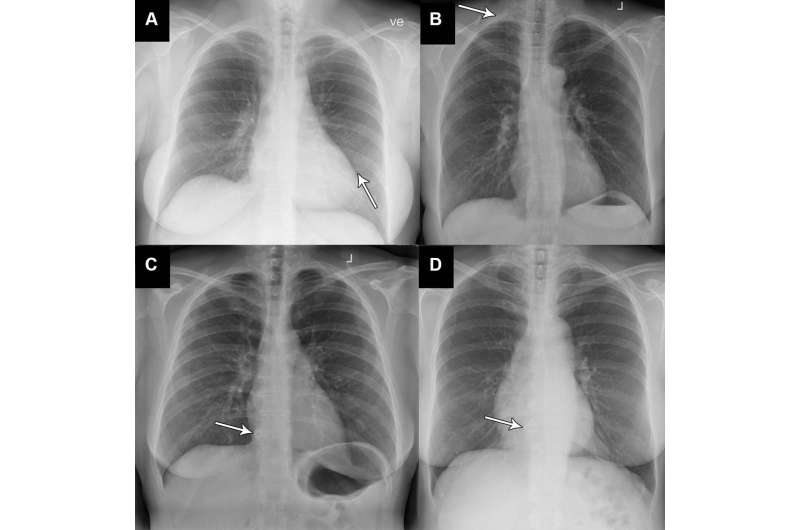
Two board-certified thoracic (chest) radiologists were used as the reference standard. A third radiologist was used in cases of disagreements, and all three physicians were blinded to the AI results.
Of the 429 chest X-rays that were classified as normal, 120, or 28%, were also classified by the AI tool as normal. These X-rays, or 7.8 % of all the X-rays, could be potentially safely automated by an AI tool. The AI tool identified abnormal chest X-rays with a 99.1% of sensitivity.
“The most surprising finding was just how sensitive this AI tool was for all kinds of chest disease,” Dr. Plesner said. “In fact, we could not find a single chest X-ray in our database where the algorithm made a major mistake. Furthermore, the AI tool had a sensitivity overall better than the clinical board-certified radiologists.”
According to the researchers, further studies could be directed toward larger prospective implementation of the AI tool where the autonomously reported chest X-rays are still reviewed by radiologists.
The AI tool performed especially well at identifying normal X-rays of the outpatient group at a rate of 11.6%. This suggests that the AI model would perform especially well in outpatient settings with a high prevalence of normal chest X-rays.
“Chest X-rays are one of the most common imaging examination performed worldwide,” Dr. Plesner said. “Even a small percentage of automatization can lead to saved time for radiologists, which they can prioritize on more complex matters.”
More information:
Louis L. Plesner et al, Autonomous Chest Radiograph Reporting Using AI: Estimation of Clinical Impact, Radiology (2023). DOI: 10.1148/radiol.222268
Journal information:
Radiology
Source: Read Full Article