Home » Health News »
Developing the first technique to find the causative agent of brain diseases
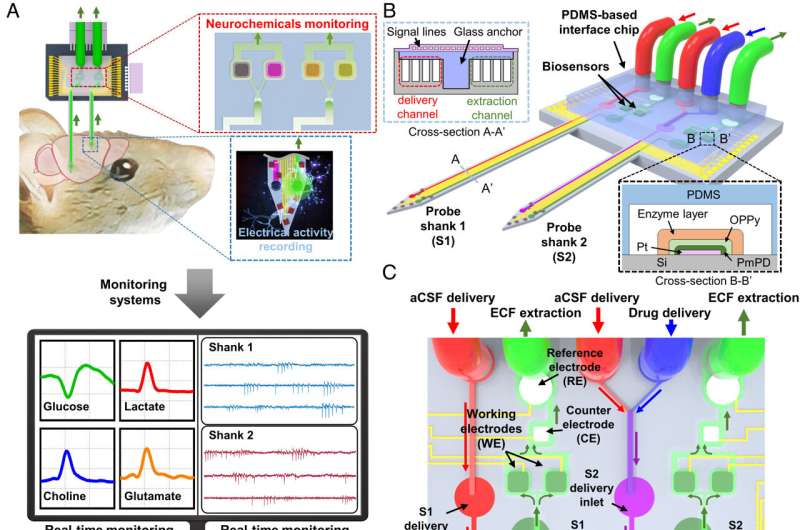
Professor Il-Joo Cho of College of Medicine, Korea University, and his research team successfully developed the first brain chip that can simultaneously measure several types of neurotransmitters in real time.
Neurotransmitters are crucial to human brain functions, and it is known that when the concentration of neurotransmitters is low or high, it causes various brain diseases due to abnormalities in the brain operation. For example, high or low levels of dopamine in specific regions of the brain cause Parkinson’s disease and schizophrenia.
In order to effectively treat such brain diseases, the concentration of neurotransmitters must be in a normal range. This implies that neurotransmitters can be utilized as a potential treatment for brain diseases. Therefore, it is necessary to precisely measure neurotransmitters in specific regions of the brain to identify the causes of various brain diseases and develop treatments.
However, precise measurement of neurotransmitters has proven challenging, especially when multiple neurotransmitters have to be measured simultaneously. This complexity has hindered the exploration of correlation between different neurotransmitters in studies.
The brain chip developed by Professor Il-Joo Cho’s team is designed to be inserted into specific regions of the brain, enabling it to measure both neurotransmitters and neural signals simultaneously. The chip incorporates a fluid tube that facilitates the extraction of cerebrospinal fluid.
Subsequently, this fluid is directed to an integrated sensor array, allowing real-time observation of various neurotransmitters present in the fluid. Remarkably, the brain chip’s small size, measuring only 0.1 mm, minimizes tissue damage upon insertion, making it approximately eight times smaller than conventional probes used for the cerebrospinal fluid extraction.
Additionally, through the application of the brain chip in a mouse test, the team successfully demonstrated the functional connectivity of neural circuits between the prefrontal cortex and thalamic region, which are brain regions associated with schizophrenia. The team also showed that these two regions are connected via excitatory glutamatergic neurons.
When the prefrontal cortex was stimulated, the team observed a subsequent increase in the concentration of glutamic acid in the thalamic region. Moreover, the team observed changes in neural signals corresponding to the activity of glutamic acid neurons.
Professor Il-Joo Cho said, “the brain chip we developed is the first system capable of real-time measurement and analysis of neural signals and various neurochemicals across multiple complex brain regions.” He further emphasized, “We expect it to be a valuable tool in the process of identifying neurotransmitters related to brain diseases and developing treatments for them.”
The findings are published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
More information:
Uikyu Chae et al, A neural probe for concurrent real-time measurement of multiple neurochemicals with electrophysiology in multiple brain regions in vivo, Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2023). DOI: 10.1073/pnas.2219231120
Journal information:
Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences
Source: Read Full Article


